Đề thi Writing ngày 9/4/2025
The diagrams below give information about two road tunnels in two Australian cities. Summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách viết bài miêu tả diagram
Hiểu yêu cầu và nội dung diagram
- Yêu cầu: Diagram yêu cầu bạn “summarize the information by selecting and reporting the main features and make comparisons where relevant” (tóm tắt thông tin bằng cách chọn và báo cáo các đặc điểm chính, đồng thời so sánh khi phù hợp).
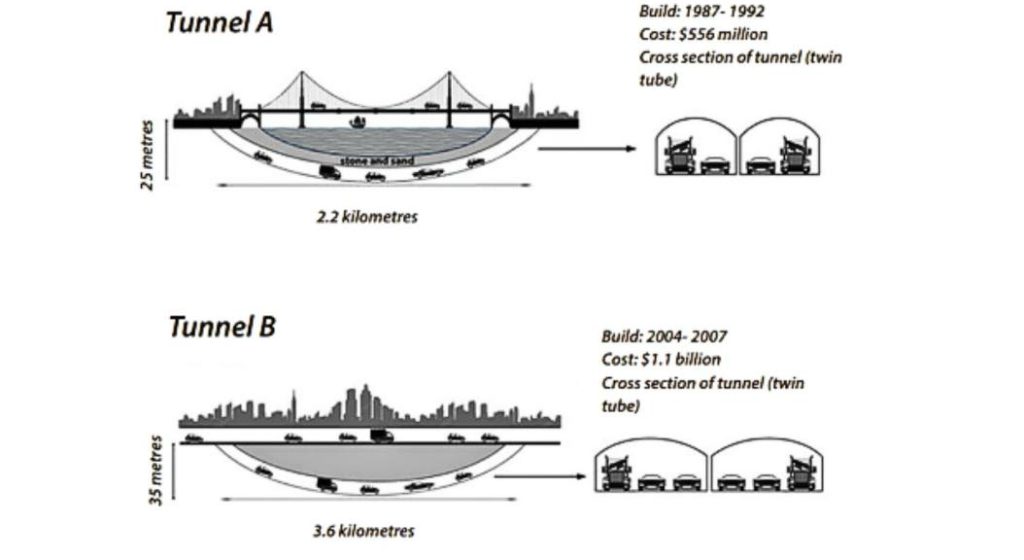
- Nội dung diagram: Diagram cung cấp thông tin về hai đường hầm (Tunnel A và Tunnel B) ở hai thành phố Úc với các chi tiết:
- Tunnel A:
- Xây dựng: 1987-1992
- Chi phí: $556 million
- Chiều dài: 2.2 km
- Độ sâu: 25 mét
- Tunnel B:
- Xây dựng: 2004-2007
- Chi phí: $1.1 billion
- Chiều dài: 3.6 km
- Độ sâu: 35 mét
- Cả hai đường hầm đều có mặt cắt ngang (cross-section) là twin tube (hai đường ống song song).
- Tunnel A:
Xác định cấu trúc bài viết
Một bài summary dạng này thường có cấu trúc 3 phần:
- Introduction (Giới thiệu): Giới thiệu ngắn gọn về nội dung diagram.
- Overview (Tổng quan): Đưa ra cái nhìn tổng quát về các đặc điểm chính hoặc xu hướng nổi bật của cả hai đường hầm mà không đi vào chi tiết cụ thể.
- Body (Thân bài): Mô tả chi tiết các đặc điểm của Tunnel A và Tunnel B, sau đó so sánh.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết từng phần
Hướng dẫn chi tiết từng phần
Bước 1: Introduction (Giới thiệu)
- Mục tiêu: Giới thiệu nội dung diagram, bao gồm các chi tiết mới.
- Ví dụ câu giới thiệu:
- “The diagram presents information about two road tunnels in two Australian cities, detailing their construction, dimensions, costs, and additional features such as bridges and surrounding developments.”
Bước 2: Overview (Tổng quan)
- Mục tiêu: Đưa ra cái nhìn tổng quát, nhấn mạnh các điểm nổi bật, bao gồm cầu dây văng ở Tunnel A và nhiều tòa nhà ở Tunnel B.
- Ví dụ đoạn Overview:
- “Overall, both tunnels feature a twin-tube design, but they differ in scale and timeline, with Tunnel A incorporating a cable-stayed bridge and Tunnel B surrounded by more modern buildings due to its later construction.”
Bước 3: Body (Thân bài)
- Mục tiêu: Mô tả chi tiết Tunnel A và Tunnel B, bao gồm các chi tiết mới, sau đó so sánh.
- Cách viết: Chia thành 2 phần:
- Phần 1: Mô tả chi tiết Tunnel A và Tunnel B (bao gồm cầu, chất liệu, số làn xe, tòa nhà).
- Phần 2: So sánh các khía cạnh chính.
Phần 1: Mô tả chi tiết
- Mẹo: Đề cập các chi tiết mới một cách logic, ví dụ: thời gian → chiều dài → độ sâu → chi phí → cầu → chất liệu → số làn xe → tòa nhà.
- Giả định hợp lý:
- Chất liệu của Tunnel A: Thường các đường hầm thời đó dùng bê tông cốt thép (reinforced concrete).
- Số làn xe: Twin-tube thường có 2 làn mỗi ống, nên giả định mỗi đường hầm có 4 làn (2 làn mỗi hướng).
- Tòa nhà ở Tunnel B: Vì Tunnel B xây muộn hơn (2004-2007), có thể có nhiều tòa nhà cao tầng (high-rise buildings) mọc lên xung quanh.
- Ví dụ đoạn mô tả:
- “Tunnel A, built from 1987 to 1992, spans 2.2 kilometers and reaches a depth of 25 meters, costing $556 million. It features a cable-stayed bridge above and is constructed using reinforced concrete, with 4 lanes in total. In contrast, Tunnel B, constructed between 2004 and 2007, extends 3.6 kilometers and descends to 35 meters, with a higher cost of $1.1 billion. Also designed with 6 lanes, Tunnel B is surrounded by numerous high-rise buildings, reflecting urban development during its construction period.”
Phần 2: So sánh
- Mẹo: So sánh các khía cạnh chính, bao gồm các chi tiết mới (cầu, tòa nhà).
- Ví dụ đoạn so sánh:
- “While Tunnel A was built over a decade earlier than Tunnel B, it is shorter and shallower, with a length of 2.2 kilometers compared to 3.6 kilometers and a depth of 25 meters compared to 35 meters. Tunnel B’s cost of $1.1 billion is nearly double Tunnel A’s $556 million, likely due to its larger scale. Additionally, Tunnel A features a cable-stayed bridge, whereas Tunnel B is notable for the high-rise buildings around it. However, both tunnels share a twin-tube design.”
Bước 4: Ghép các phần thành bài hoàn chỉnh
The diagram presents information about two road tunnels in two Australian cities, detailing their construction, dimensions, costs, and additional features such as bridges and surrounding developments.
Overall, both tunnels feature a twin-tube design, but they differ in scale and timeline, with Tunnel A incorporating a cable-stayed bridge and Tunnel B surrounded by more modern buildings due to its later construction.
Tunnel A, built from 1987 to 1992, spans 2.2 kilometers and reaches a depth of 25 meters, costing $556 million. It features a cable-stayed bridge above and is constructed using reinforced concrete, with four lanes in total. In contrast, Tunnel B, constructed between 2004 and 2007, extends 3.6 kilometers and descends to 35 meters, with a higher cost of $1.1 billion. Also designed with six lanes, Tunnel B is surrounded by numerous high-rise buildings, reflecting urban development during its construction period. While Tunnel A was built over a decade earlier than Tunnel B, it is shorter and shallower, with a length of 2.2 kilometers compared to 3.6 kilometers and a depth of 25 meters compared to 35 meters. Tunnel B’s cost is nearly double Tunnel A’s, likely due to its larger scale. Additionally, Tunnel A features a cable-stayed bridge, whereas Tunnel B is notable for the high-rise buildings around it. However, both tunnels share a twin-tube design.